A Reverb simulates the component of sound that results from reflections from surrounding walls or objects. It is in effect a room simulator. Some people think it's just a delay effect with some filters, but it's way more complex than that.
There are three possible reasons for adding reverb:
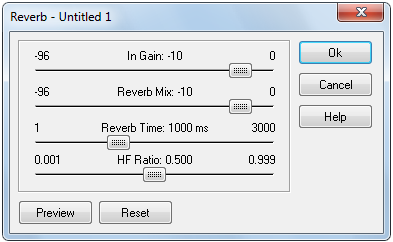
Reverb controls
In Gain: sets the input gain of signal, in decibels (dB)
Reverb Mix: sets the reverb mix, in decibels (dB). At zero there is no effect (Dry). At 100% only the processed reverb signal (Wet) is produced.
Reverb Time: sets the reverb time, in milliseconds. Short reverb times simulate small room reflections. Use longer reverb time to simulate larger spaces
HF Ratio: sets the high-frequency reverb time ratio Low values create a hard reverb suitable for producing small "bathroom" type reverbs. Higher values produce a softer reverb suitable for simulating large spaces such as Cathedrals.
|
Copyright (c) 2013 AudioDope team. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|