Waveform Audio File Format (WAVE, or more commonly known as WAV due to its filename extension) is a Microsoft and IBM audio file format standard for storing an audio bitstream on PCs. It is an application of the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF) bitstream format method for storing data in "chunks" It is the main format used on Windows systems for raw and typically uncompressed audio. The usual bitstream encoding is the linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM) format.
WAV is compatible with Windows, Macintosh, and Linux operating systems. The format takes into account some differences of the Intel CPU such as little-endian byte order. The RIFF format acts as a "wrapper" for various audio compression codecs.
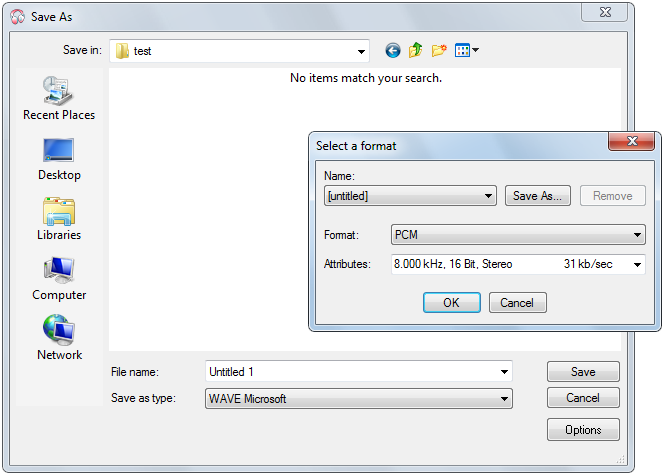
Though a WAV file can hold compressed audio, the most common WAV format contains uncompressed audio in the linear pulse code modulation (LPCM) format. The standard audio file format for CDs, for example, is LPCM-encoded, containing two channels of 44,100 samples per second, 16 bits per sample. Since LPCM uses an uncompressed storage method which keeps all the samples of an audio track, professional users or audio experts may use the WAV format for maximum audio quality. WAV audio can also be edited and manipulated with relative ease using software. The WAV format supports compressed audio, using, on Windows, the Audio Compression Manager. Any ACM codec can be used to compress a WAV file. The user interface (UI) for Audio Compression Manager may be accessed through clicking the “Options” button at the “Save as” dialog.
Uncompressed WAV files are large, so file sharing of WAV files over the Internet is uncommon. However, it is a commonly used file type, suitable for retaining first generation archived files of high quality, for use on a system where disk space is not a constraint, or in applications such as audio editing, where the time involved in compressing and uncompressing data is a concern.
More frequently, the smaller file sizes of compressed but lossy formats such as MP3 are used to store and transfer audio. Their small file sizes allow faster Internet transmission, as well as lower consumption of space on memory media. There are also lossless formats but there is no ubiquitous standard among these for either professional or home audio.
The WAV format is limited to files that are less than 4 GB, because of its use of a 32-bit unsigned integer to record the file size header This is equivalent to about 6.8 hours of CD-quality audio (44.1 kHz, 16-bit stereo).
As mentioned wav files can be encoded with a variety of codecs to reduce the file size (for example the GSM or MP3 codecs).
This is a reference to compare the monophonic (not stereophonic) audio quality and compression bitrates of the different codecs available for .wav files including PCM, ADPCM, Microsoft GSM 06.10, CELP, SBC, Truespeech and MPEG Layer-3.
Attention
Not all acm codecs can be used to convert from one format to another. In such a case you will take a message “Conversion not possible”
|
Copyright (c) 2013 AudioDope team. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|